4 Aspect-oriented Spring
4.1 面向切面编程
像日志、安全、事务这些跨越多个应用组件的公共功能,单独抽出来,形成切面,这样应用组件只需要关注自己的业务逻辑。
AOP术语
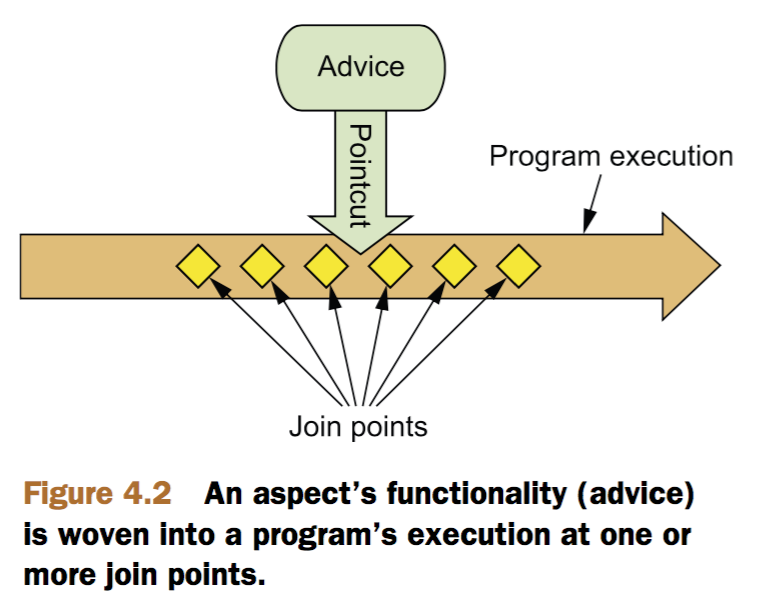
Advice
是切面的主要任务,包括做什么(what)和何时做(when),有5种advice:
- Before—The advice functionality takes place before the advised method is invoked.
- After—The advice functionality takes place after the advised method completes, regardless of the outcome.
- After-returning—The advice functionality takes place after the advised method successfully completes.
- After-throwing—The advice functionality takes place after the advised method throws an exception.
- Around—The advice wraps the advised method, providing some functionality before and after the advised method is invoked.
Join points
是应用执行流程中切面可以插入的点,比如一个方法被调用、一个异常被抛出,甚至一个字段被修改。
Pointcuts
pointcuts定义了切面的where,一个pointcut定义匹配一个或多个join points,表示切面需要织入的地方。
Aspects
切面是advice和pointcuts的混合。
Introductions
introduction允许你添加新的方法和属性到已有的类。
Weaving
Weaving是把切面应用到目标对象创建新的代理对象的过程,织入可以发生在目标对象生命周期的几个时间点:
- Compile time—Aspects are woven in when the target class is compiled. This requires a special compiler. AspectJ’s weaving compiler weaves aspects this way.
- Class load time—Aspects are woven in when the target class is loaded into the JVM. This requires a special ClassLoader that enhances the target class’s byte-code before the class is introduced into the application. AspectJ 5’s load-time weaving (LTW) support weaves aspects this way.
- Runtime—Aspects are woven in sometime during the execution of the application. Typically, an AOP container dynamically generates a proxy object that delegates to the target object while weaving in the aspects. This is how Spring AOP aspects are woven.
Spring支持4种形式的AOP:
- Classic Spring proxy-based AOP
- Pure-POJO aspects
- @AspectJ annotation-driven aspects
- Injected AspectJ aspects (available in all versions of Spring)
前三种是Spring自己的AOP实现,Spring AOP基于动态代理,因此,仅限于方法拦截。如果你需要构造器或者属性拦截,你可以考虑使用AspectJ。
Spring的切面就是标准的Java类,而AspectJ有特定的AOP语言。

4.2 Selecting join points with pointcuts
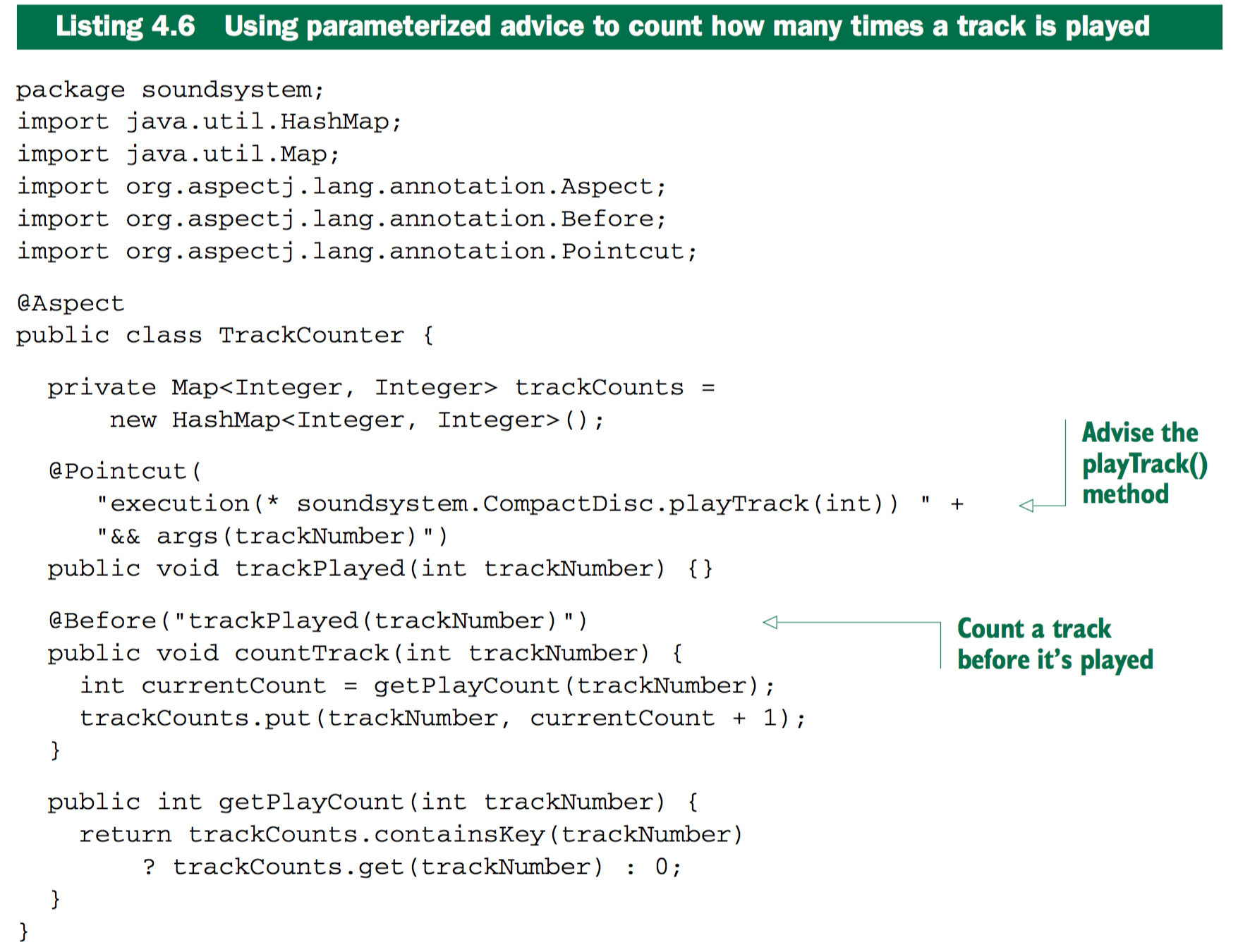
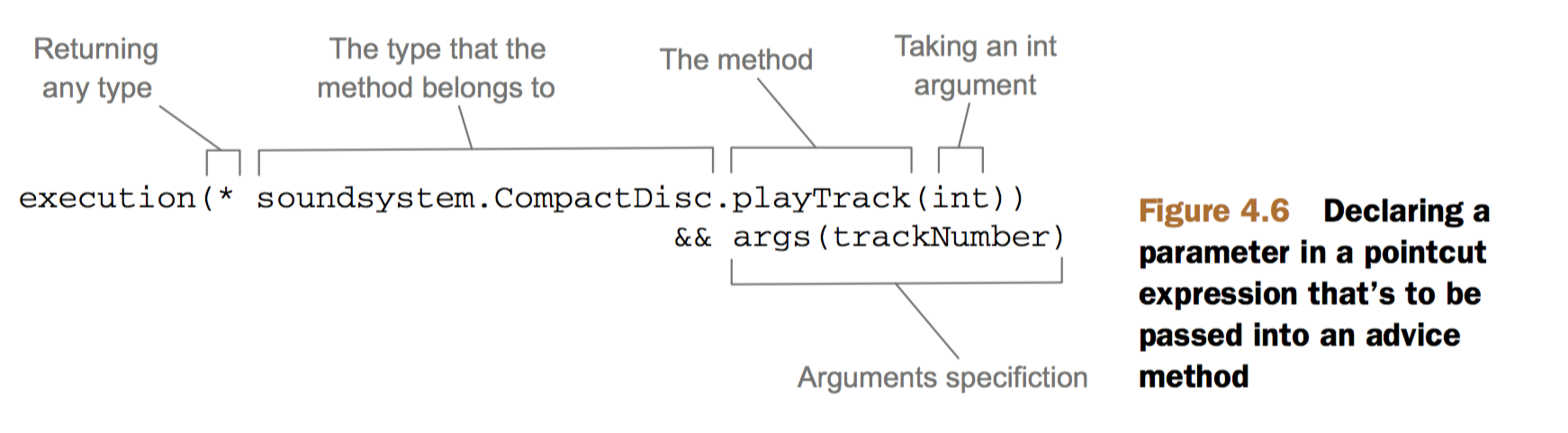
Spring AOP中,使用AspectJ的切点表达式语言来定义pointcuts



除了4.1中的标识符,Spring添加了bean()标识符,可以在切点表达式中指定具体的bean ID。
4.3 Creating annotated aspects
给一个POJO类加上注解 @Aspect 就能创建一个切面,给方法加上切点:
@Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void silenceCellPhones() {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phones");
}

在每一个地方都标注上相同的切点表达式就太繁琐了,可以使用 @Pointcut 注解在一个地方定义好:

配置自动代理:

创建around advice:

别忘了调用jd.proceed()来调用被代理的方法!否则会阻塞被代理方法的调用,你也可以多次调用被代理方法,一种理由是实现重试逻辑。
AOP introductions


EncoreableIntroducer把 Encoreable 接口引入了 Performance bean。
4.4 XML配置
略。
4.5 注入AspectJ切面
使用AspectJ定义的切面往往需要注入Spring的beans,但是AspectJ的切面是由AspectJ运行时创建的,所以没法被Spring上下文拿到,好在所有的AspectJ切面都提供了一个静态的工厂方法aspectOf(),返回那个切面的单实例,所以可以这样注入:
<bean class="com.springinaction.springidol.CriticAspect" factory-method="aspectOf">
<property name="criticismEngine" ref="criticismEngine" />
</bean>